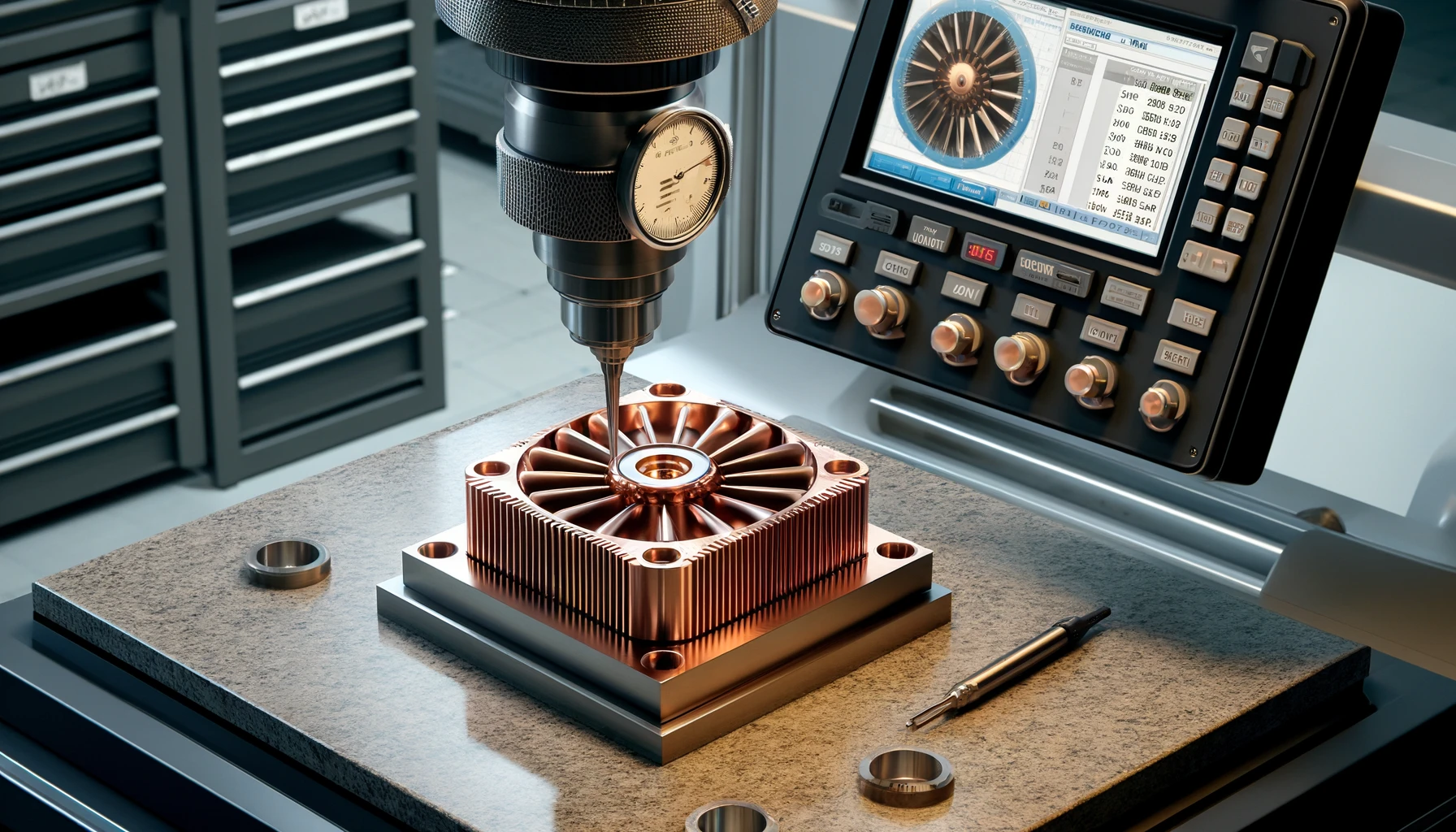
Understanding the Technical Challenges in CNC Machining Copper Heat Sinks
Machining copper heat sinks presents several challenges due to the material’s softness, tendency to adhere to tools, and high thermal conductivity. Ensuring precision during CNC machining requires advanced equipment, skilled operators, and stringent quality control measures to maintain tight tolerances and achieve the required surface finishes.
Why is Precision Important in Quality Control for Copper Heat Sinks?
Precision is crucial for copper heat sinks as it directly impacts thermal efficiency. Tight tolerances ensure that heat sinks fit perfectly with other components, optimizing heat transfer. Deviations can lead to inefficient cooling and impact the device’s performance. For instance, a study showed that heat sinks with dimensional tolerances within ±0.01mm had up to 20% better heat transfer than those with looser tolerances.
What CNC Machine Features Are Essential for Quality Control of Copper Heat Sinks?
- High-Speed Spindles: Maintain precise cuts, reducing tool wear and ensuring smooth surfaces.
- Advanced Cooling Systems: Manage heat generation to prevent tool wear and material distortion.
- Tool Holding Systems: Minimize runout, maintaining consistent precision.
- Adaptive Control Systems: Adjust machining parameters in real-time for consistent quality.
Case Study: A precision electronics manufacturer used high-speed spindles with advanced cooling systems to produce heat sinks with tolerances within ±0.005mm, enabling their product to achieve a 30% improvement in heat dissipation.
What Testing and Inspection Methods Should Be Used for Copper Heat Sinks?
- Dimensional Inspection: CMMs verify critical dimensions to ensure geometric accuracy.
- Surface Finish Evaluation: Profilometers measure roughness to ensure thermal efficiency.
- Non-Destructive Testing: Ultrasonic and eddy current testing detect internal defects.
- Metallurgical Testing: Chemical composition and microstructure analysis ensure material quality.
Testing and Inspection Methods Table:
| Method | Accuracy (Microns) | Purpose | Use Case | Common Tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMM | ±1 | Dimensional accuracy | Critical dimensions | Coordinate measuring machine |
| Profilometer | ±0.1 | Surface roughness | Surface quality | Surface profilometer |
| Ultrasonic Testing | N/A | Internal defects | Material integrity | Ultrasonic flaw detector |
| Eddy Current Testing | N/A | Conductivity and defects | Material quality | Eddy current tester |
| Microhardness Tester | ±0.01 | Material hardness | Heat treatment analysis | Microhardness tester |
| Spectroscopy | N/A | Chemical composition | Alloy verification | Optical emission spectrometer |
How to Ensure Consistent Quality in Copper Heat Sink Production?
- Standardized Processes: Implementing standard operating procedures ensures consistency.
- Automation: Automated CNC machines reduce human error and maintain precision.
- Process Monitoring: Real-time monitoring identifies deviations early, minimizing waste.
Case Study: A leading CNC machining company adopted automated tool paths and real-time monitoring, reducing defect rates by 20% and improving efficiency by 30%.
What Are the Common Defects in Copper Heat Sinks and How to Avoid Them?
- Burrs: Result from improper tooling or feeds, removed by deburring tools.
- Tool Marks: Tool chatter or incorrect speeds and feeds cause marks.
- Surface Oxidation: Prevented by using the correct coolant and proper storage.
- Cracks: Caused by improper heat treatment or machining stresses.
Common Defects Table:
| Defect Type | Cause | Impact | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Burrs | Incorrect feeds or tooling | Rough edges | Adjusting cutting parameters |
| Tool Marks | Tool chatter | Poor surface finish | Optimizing speeds and feeds |
| Surface Oxidation | Exposure to air and moisture | Reduced heat transfer | Proper coolant and storage |
| Cracks | Machining stress | Reduced structural integrity | Proper heat treatment |
| Dimensional Errors | Machine vibration | Improper fit | Regular machine maintenance |
| Warping | Heat from machining | Distortion | Optimized coolant and tool paths |
How to Develop a Comprehensive Quality Control Plan for Copper Heat Sinks?
- Material Testing: Ensure copper quality through chemical composition and hardness testing.
- Process Control: Implement strict process controls for machining and heat treatment.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect parts for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and defects.
- Documentation: Maintain records of quality control processes for traceability.
What Are the Key Considerations When Choosing a CNC Machining Supplier for Copper Heat Sinks?
- Technical Expertise: Look for suppliers with experience in precision copper machining.
- Quality Certifications: Ensure suppliers have ISO certifications indicating quality control.
- Production Capacity: Consider the supplier’s ability to handle your volume requirements.
- Geographic Location: Proximity to your manufacturing facility can reduce shipping time and costs.
Supplier Comparison Table:
| Supplier Name | ISO Certification | Production Capacity (Units/Month) | Location | Specialization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CopperTech Inc. | ISO 9001 | 50000 | USA | High-precision machining |
| HeatSink Solutions | ISO 14001 | 75000 | Japan | Complex heat sinks |
| PrecisionCopper | ISO 9001 | 30000 | Germany | Custom copper parts |
| ThermoMachining | ISO 14001 | 100000 | China | High-volume production |
| MultiAxis Mfg. | ISO 9001 | 20000 | UK | Multi-axis machining |
| Copper Machining Co. | ISO 9001 | 40000 | India | Medium-volume production |
Related Posts
- How to Choose the Right CNC Machining Service for Precision Copper Heat Sinks?
Understanding the Technical Challenges in Machining Copper Heat Sinks Copper heat sinks are crucial in various electronic applications because of their superior thermal conductivity. However, this same property makes copper…
- How to Choose the Right CNC Machining Partner for Manufacturing Copper Heat Sinks?
What Technical Expertise Should You Look for in a CNC Machining Partner for Copper Heat Sinks? CNC machining of copper heat sinks presents unique technical challenges due to the material's…
- What Should Buyers Look for in a CNC Machining Company for Precision Copper Heat Sinks?
Understanding the Global Technical Challenges of Machining Copper Heat Sinks Global buyers seeking CNC machining suppliers for copper heat sinks face unique challenges due to variations in technical expertise, machinery…
- The Dependable Quality Assurance in China CNC Machining
1. Introduction: Setting the Stage for Quality Excellence In this introductory section, we lay the groundwork for an exploration into the world of quality assurance in China CNC machining. We…
- Bead Blasting: The Secret to Quality CNC Machining(cnc machining tools Mavis)
The world of manufacturing has witnessed revolutionary changes with the advent of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining. It is a process used in the manufacturing sector that involves the use…
- Zinc Alloys in CNC Machining: Benefits and Limitations
Introduction - CNC Machining and Zinc Alloys Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is a highly precise manufacturing process widely utilized in various industries to create complex parts. It makes use…