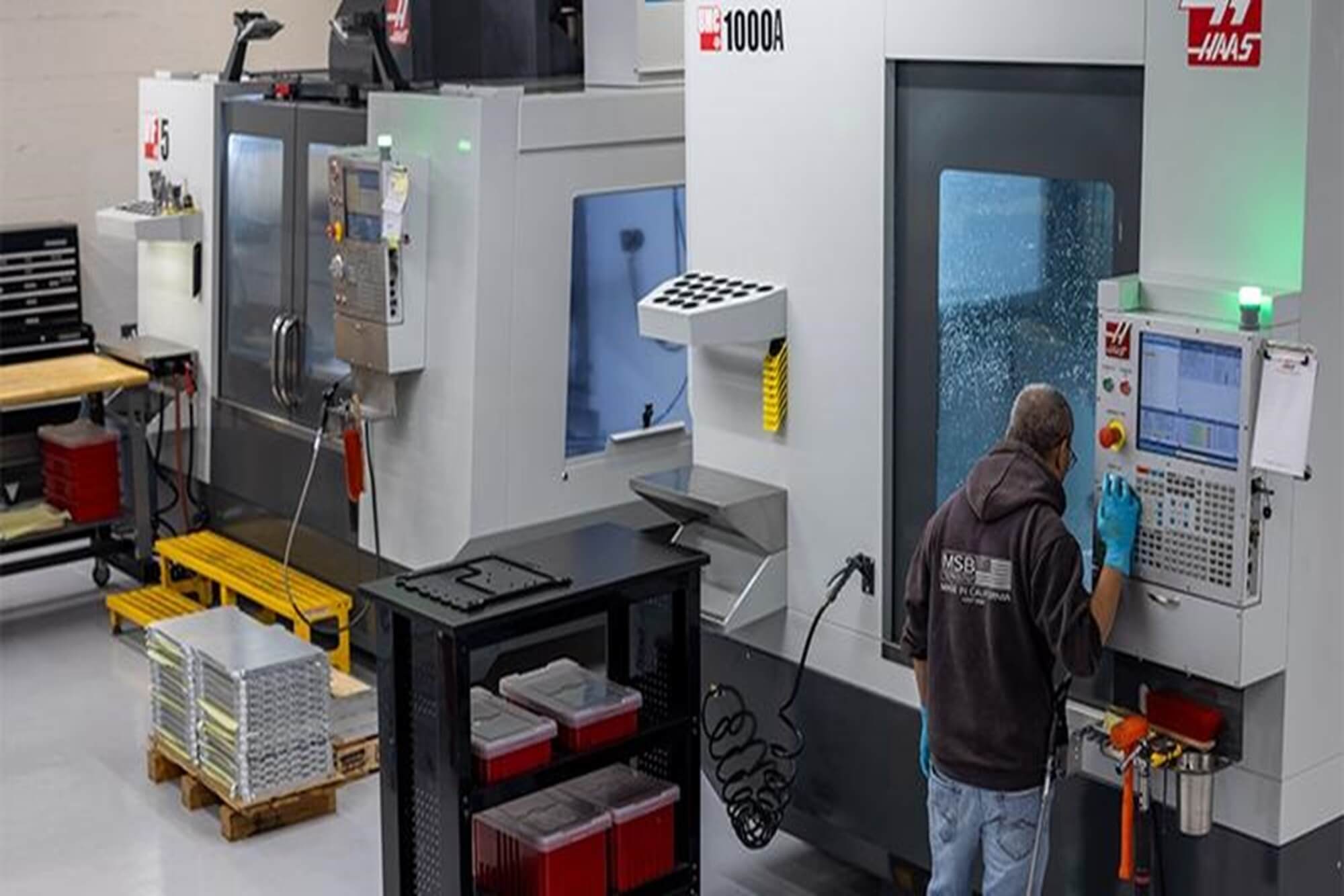
Turning a digital design into a tangible, high-precision component is a challenge I’ve encountered countless times in my career as an engineer. Whether you’re a startup founder sketching ideas or a seasoned product developer refining a prototype, a CNC machine shop is your bridge to reality. These shops don’t just cut metal or plastic—they transform concepts into functional parts with exacting standards. In this guide, I’ll share insights from my experience working with CNC machine shops, explore the intricacies of CNC machining, and provide a roadmap for leveraging their capabilities. From processes and materials to industry applications and future trends, I’ll blend technical depth with practical advice, including first-hand lessons learned, to help you navigate this dynamic field.
The Heart of Precision: What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining, or Computer Numerical Control machining, is a subtractive manufacturing process where computer-guided tools sculpt a workpiece into a precise part. In a CNC machine shop, it starts with a digital CAD model, which CAM software translates into G-code—a language that directs every tool movement with pinpoint accuracy. I’ve watched machinists at a CNC machine shop I collaborated with turn a rough aluminum block into a medical device component with tolerances tighter than a human hair. This precision, combined with automation, allows CNC machining to produce complex geometries consistently, far surpassing manual methods.
The real magic of CNC machining lies in its versatility. Early in my career, I underestimated its potential, assuming it was limited to basic parts. But after visiting a CNC machine shop in California, I saw firsthand how CNC machining crafted intricate aerospace brackets in a single setup—something manual machining could never achieve. The process offers unmatched precision (tolerances as low as +/- 0.01 mm), the ability to handle complex designs, and efficiency through automated operations, often running 24/7 in “lights-out” mode. For businesses, this translates to faster timelines, lower costs over time, and safer workflows due to enclosed systems.
Why CNC Machine Shops Are Game-Changers
Partnering with a CNC machine shop revolutionized how I approached product development. Unlike traditional machining, which relies on human skill and is prone to inconsistency, CNC machining ensures repeatability across thousands of parts. I recall a project where we needed 500 identical titanium implants for a medical client. The CNC machine shop delivered every piece within spec, saving weeks compared to manual methods. Additionally, CNC machining handles intricate designs—like curved turbine blades—that would stump even the most skilled machinist. The automation also reduces labor costs and material waste, making it a sustainable choice in today’s eco-conscious market.
Services That Power Innovation
A CNC machine shop is more than a workshop; it’s a hub of solutions tailored to your project’s needs. From prototyping to high-volume production, these shops offer flexibility that I’ve found invaluable. For instance, when I needed a single prototype for a robotics component, the CNC machine shop I worked with delivered it in days, allowing us to test and iterate quickly. For larger runs, their scalability ensures consistent quality, whether producing 10 or 10,000 parts.
Core Processes: Milling and Turning
The backbone of CNC machining includes milling and turning. In milling, a rotating tool carves a stationary workpiece. I’ve seen 3-axis milling used for straightforward parts like brackets, but 5-axis milling—available at top-tier CNC machine shops—is a game-changer for complex shapes, like aerospace housings, machined in one go to avoid errors. Turning, on the other hand, spins the workpiece against a stationary tool, perfect for cylindrical parts like shafts. I once oversaw a project where a CNC machine shop used turning to produce precision pins for an automotive assembly, meeting specs that manual lathes couldn’t touch.
Beyond the Basics: Specialized Techniques
Advanced CNC machine shops also offer processes like Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM). I was skeptical of EDM until I saw it in action during a shop visit. It uses electrical sparks to erode hard metals like titanium without physical force, ideal for delicate or intricate parts. For a medical tool project, EDM allowed us to create sharp internal corners that standard CNC machining couldn’t achieve, proving its value for niche applications.
Materials: The Foundation of Function
Choosing the right material in a CNC machine shop is as critical as the machining process itself. Metals like aluminum (6061 for versatility, 7075 for aerospace-grade strength), stainless steel (304 for corrosion resistance), and titanium (for lightweight durability) are staples. Plastics like ABS, Nylon, POM (Delrin), and PEEK offer unique properties for specific needs. I learned this the hard way when I initially chose a cheaper plastic for a prototype, only to find it warped under stress. After consulting with the CNC machine shop, we switched to PEEK for its heat resistance, which saved the project.
Table 1: Comparative Guide to Common CNC Machining Materials (exportable to Google Sheets)
| Material | Key Properties | Common Applications | Relative Cost | Machinability |
| Aluminum 6061 | Excellent strength-to-weight, corrosion resistant | Automotive, electronics | $$ | ★★★★★ |
| Stainless Steel 304 | High strength, corrosion resistant | Medical devices, hardware | $$$ | ★★★ |
| Mild Steel 1018 | Good strength, highly machinable | Jigs, fixtures | $ | ★★★★ |
| Titanium (Grade 5) | High strength-to-weight, corrosion resistant | Aerospace, medical implants | $$$$$ | ★★ |
| Brass C360 | Low friction, conductive | Fittings, electrical contacts | $$$ | ★★★★★ |
| ABS | High impact strength, rigid | Prototypes, enclosures | $ | ★★★★ |
| Nylon 6/6 | High strength, wear resistant | Gears, bearings | $$ | ★★★ |
| POM (Delrin) | High stiffness, low friction | Precision gears, medical devices | $$ | ★★★★★ |
| PEEK | High temperature/chemical resistance | Aerospace, medical implants | $$$$$ | ★★ |
Surface Finishes: The Final Touch
A part fresh from CNC machining is functional but often needs finishing to meet aesthetic or performance requirements. In my experience, choosing the right finish can make or break a part’s success. For example, a CNC machine shop once suggested anodizing for an aluminum prototype to enhance its durability and appearance, which impressed our client. Options include as-machined (with minor tool marks), bead blasting for a matte look, anodizing for corrosion resistance, and powder coating for vibrant, durable surfaces.
Industry Impact: Where CNC Machining Shines
CNC machine shops are indispensable across industries. In aerospace, they craft flight-critical components like turbine blades. In medical, they produce implants with biocompatible materials. I’ve worked on automotive projects where CNC machining delivered engine parts with precision that ensured performance under extreme conditions. Consumer electronics, energy, robotics, and even agriculture rely on CNC machine shops for everything from smartphone casings to durable wind turbine components. The ability to scale from prototypes to mass production makes CNC machining a cornerstone of innovation.
Choosing the Right CNC Machine Shop
Finding the right CNC machine shop is a make-or-break decision. I’ve learned to prioritize expertise, equipment, and communication over cost alone. A shop with experience in your industry—say, medical or aerospace—understands your unique needs. Advanced equipment, like 5-axis mills or CMM inspection tools, ensures precision. Certifications like ISO 9001 or AS9100 signal robust quality systems. Most importantly, a shop that offers Design for Manufacturability (DFM) feedback can save thousands. On one project, DFM suggestions from a CNC machine shop simplified a part’s geometry, cutting costs by 20% without compromising quality.
Table 3: CNC Machine Shop Vetting Checklist (exportable to Google Sheets)
| Category | Key Question | What to Look For |
| Experience | Examples of industry projects? | Relevant portfolio, client testimonials |
| Equipment | Key machines and inspection tools? | 5-axis mills, CMM, adherence to accuracy standards |
| Quality Systems | ISO 9001/AS9100 certified? | Valid certifications, documented QMS |
| Quality Control | Process for ensuring quality? | Multi-stage inspections, transparent metrics |
| Lead Time | Realistic lead times? | Transparent scheduling, flexibility |
| Communication | DFM feedback offered? | Dedicated contact, proactive suggestions |
| Security | IP protection measures? | Secure portals, cybersecurity policies |
Practical Tips from Experience
- Simplify Designs: Complex features increase costs. I once reduced machining time by 30% by streamlining a part’s geometry.
- Material Matters: Choose cost-effective options like Aluminum 6061 for non-critical parts, as I did for a consumer electronics prototype.
- Build Relationships: A trusted CNC machine shop becomes an extension of your team, offering insights that save time and money.
The Future of CNC Machining
The CNC machine shop of tomorrow is smarter and greener. Industry 4.0 technologies, like AI-optimized toolpaths and IoT-enabled monitoring, are transforming operations. I recently toured a CNC machine shop using AI to predict tool wear, reducing downtime significantly. Sustainability is also key—shops are minimizing waste through efficient programming and energy-saving machines. On-demand platforms are making CNC machining more accessible, connecting businesses to vetted shops instantly. Reshoring trends further strengthen supply chains, a shift I’ve seen reduce lead times for clients.
Conclusion: Partnering for Success
From my first project to today, CNC machine shops have been pivotal in bringing ideas to life. Their ability to deliver precision, handle complexity, and scale production is unmatched. By choosing a CNC machine shop with expertise, advanced CNC machining capabilities, and a commitment to quality, you can turn concepts into reality. As technology evolves, CNC machine shops will lead the charge, blending innovation with precision to shape the future of manufacturing.
FAQ:
1. What is a CNC machine shop, and how does it work?
A CNC machine shop uses CNC machining, a process where computer-guided tools shape parts by removing material from a workpiece. From my experience, it starts with a CAD model converted into G-code, which directs tools with precision down to +/- 0.01 mm. The shop’s machines, like mills or lathes, execute these instructions to create everything from prototypes to mass-produced components, offering unmatched accuracy and efficiency.
2. What types of services do CNC machine shops offer?
CNC machine shops provide a range of services, including prototyping, full-scale production, milling, turning, and specialized processes like Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM). I’ve seen shops deliver single prototypes in days and scale up to thousands of parts, catering to industries like aerospace and medical with no minimum order requirements.
3. What materials can a CNC machine shop work with?
A CNC machine shop handles metals like aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, brass, and copper, as well as plastics like ABS, Nylon, POM (Delrin), and PEEK. In one project, I switched to PEEK for its heat resistance after a cheaper plastic failed, a decision guided by the shop’s expertise. Material choice depends on strength, weight, or environmental needs.
4. How precise is CNC machining compared to manual methods?
CNC machining achieves tolerances as tight as +/- 0.01 mm, far surpassing manual machining. I recall a CNC machine shop producing 500 identical titanium implants with zero deviations, something impossible manually. This precision and repeatability make CNC machine shops ideal for high-stakes applications.
5. What are the benefits of using a CNC machine shop?
Partnering with a CNC machine shop offers precision, the ability to create complex geometries, and efficient production through automation. In my experience, automation reduced costs by 20% on a project by minimizing waste. Shops also enhance safety with enclosed systems and provide scalability for prototypes or large runs.
6. How do I choose the right CNC machine shop for my project?
Look for a CNC machine shop with industry-specific expertise, advanced equipment like 5-axis mills, and certifications like ISO 9001 or AS9100. I always prioritize shops offering Design for Manufacturability (DFM) feedback, as it saved me thousands on a robotics project by simplifying part geometry. Check their portfolio and communication style too.
7. What surface finishes can a CNC machine shop provide?
CNC machine shops offer finishes like as-machined, bead blasting, anodizing, powder coating, and electroplating to enhance aesthetics or durability. For an aluminum prototype, I chose anodizing based on a shop’s advice, improving both its look and corrosion resistance. The right finish depends on your part’s function and material.
Reference:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Machine_shop;
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_numerical_control;
https://wikifactory.com/+wikifactory/stories/what-is-cnc-and-everything-you-need-to-know-about-cnc;
https://blog.csdn.net/zwlzyhzylzyl/article/details/131409012;
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Geometric Secrets of CNC Machining Parts: Detailed Guide to Machine Tool Axes
When you step into the world of CNC machining, you quickly realize the importance of geometric precision. The relationship between a machine’s fixed points and the movable points of a…
- Improve the Precision of Your CNC parts
In some industries, precision machining is more essential than in others. For example, medical devices, certain parts, and products must be reliable and always work. The doctor must direct the…
- The Ultimate Guide to Acquiring CNC Machined Parts
In today's business landscape, there are two main categories: production and services. While service-based businesses are easier to establish, production businesses hold greater potential for growth. If you're considering venturing…
- The Application of Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) in Modern Machine Shops
Precision plays a crucial role in today's CNC machining industry, with measurements reaching tenths of microns and continually increasing. As machine tools become more precise, accurately measuring the deviation of…
- 11 Tools to Start A Machine Shop in US
The growth of CNC machine shops in recent years has challenged traditional manufacturing. CNC shops are small firms that use modern machinery to create metal and plastic products. They are…