CNC milling is a widely used method for manufacturing high-precision components, offering fast creation of complex surfaces. However, this craft requires continuous learning due to various issues that can compromise the quality of the workpiece and even damage the cutting tool. In this article, we will discuss four common defects encountered in CNC milling and provide effective solutions to address them.
Dents Left From Tooling
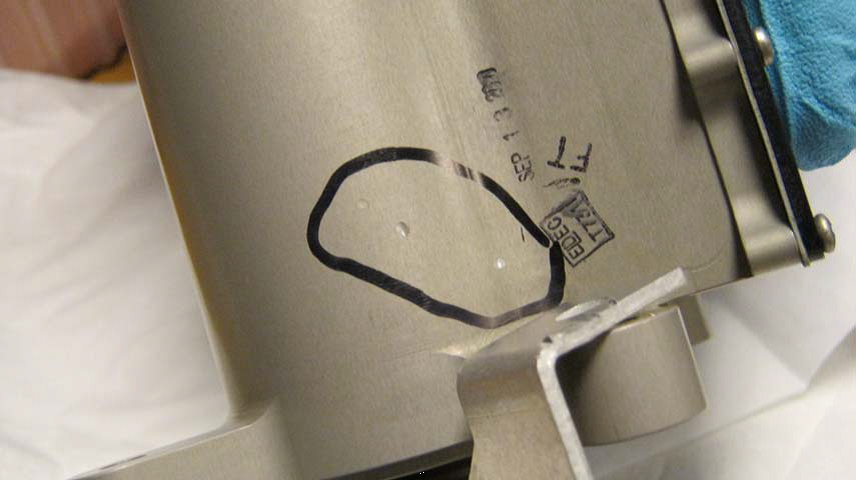

One noticeable defect that can occur during CNC milling is the presence of dents on the workpiece where clamping took place. This issue is commonly observed when working with brass, copper, bronze, or aluminum alloys.
Cause:
Excessive clamping forces exerted during the milling process lead to these dents. While manual tooling allows for better control, CNC machines often utilize pneumatic or hydraulic clamping, resulting in higher forces.
Solutions:
To prevent dents caused by pneumatic or hydraulic clamping, you can employ the following solutions:
- Intermediate Steel Plate: Place an intermediate steel plate between the workpiece and the tooling jigs to distribute pressure evenly and minimize deformations. This plate helps increase the contact area, preventing dents on the workpiece.
- Special Chucks and Jigs: Invest in specialized chucks and jigs that are softer. Even if deformation occurs, these softer tooling options won’t damage the workpiece.
Varying Surface Finish on a Single Surface
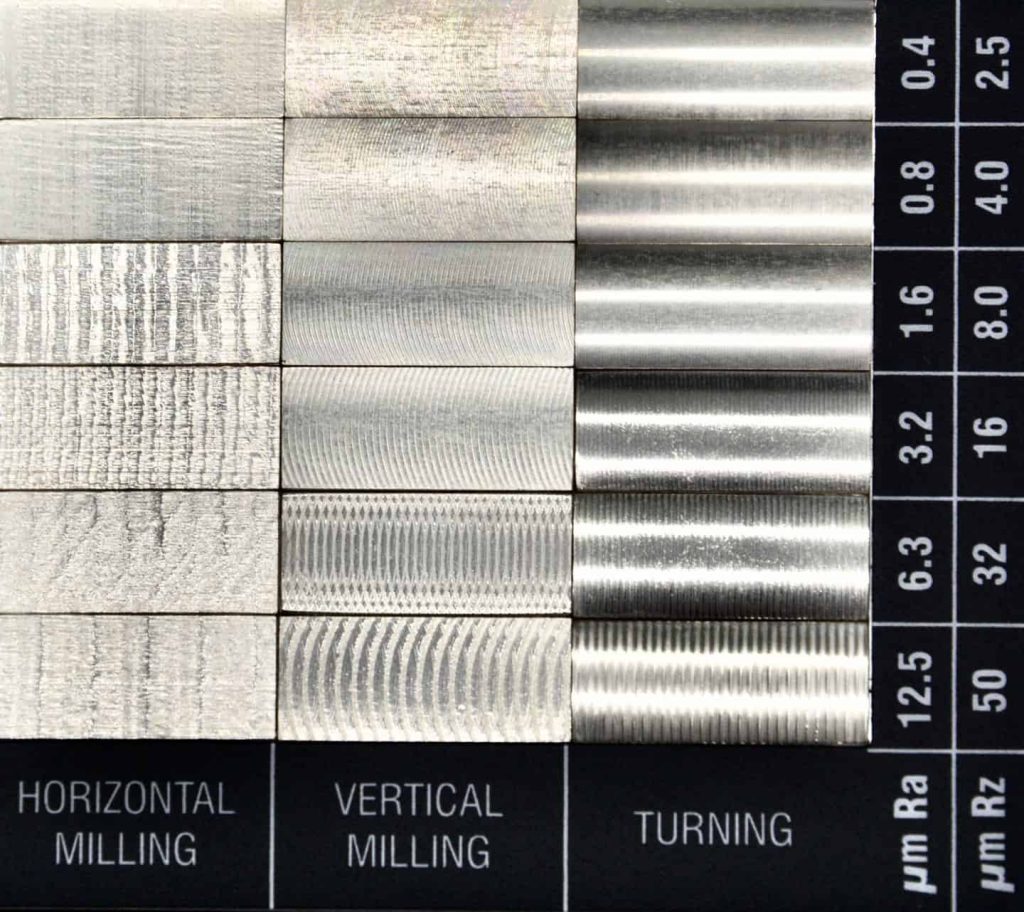

Another common issue in CNC milling relates to inconsistent surface finishes on a workpiece.
Cause:
This problem can arise due to chatter, which refers to excessive vibrations in the machine or cutter. Blunt tools can amplify the issue by causing more deformation before chip detachment. The choice of milling strategy, whether climb or conventional, can also impact surface finish. New operators sometimes unintentionally combine both strategies, resulting in a mix of smoother and rougher surfaces. Furthermore, the absence or poor choice of coolants can negatively affect surface quality.
Solution:
To achieve a smoother surface finish, you can implement the following solutions:
- Tool Maintenance: Ensure the cutting tools are sharp and in good condition. Blunt tools contribute to increased deformation and poor surface finish.
- Appropriate Milling Strategy: Choose the appropriate milling strategy based on the desired surface finish. Climb milling, where the tool enters the workpiece with a hit and exits slowly, can result in a superior surface finish. Conventional milling, on the other hand, may lead to rougher surfaces due to slight vibrations and process variations.
- Effective Coolant Usage: Use suitable coolant lubricants to enhance surface quality. Opt for quality coolants instead of underestimating their role or settling for cheaper alternatives. Proper cooling and lubrication can significantly improve the surface finish.
Burns on the Surface of the Workpiece
Burns along the surface of the machined part indicate overheating, which is a common defect in CNC milling.
Cause:
Incorrect cutting parameters, such as an unsuitable combination of feed and speed, can lead to overheating. This can cause damage to the workpiece, cutting tool, and even the machine itself.
Solution:
To address this issue, you can adopt the following solutions:
- Optimized Cutting Speed to Feed Ratio: Lower the cutting speed to feed ratio to reduce the temperature generated during the machining process. Slowing down the process can help minimize the occurrence of burns.
- Improved Cooling: Enhance the cooling rate of the process to prevent overheating. Consider the specific material being machined, as some materials, like titanium, conduct heat poorly and require extra attention to cooling.
Burrs
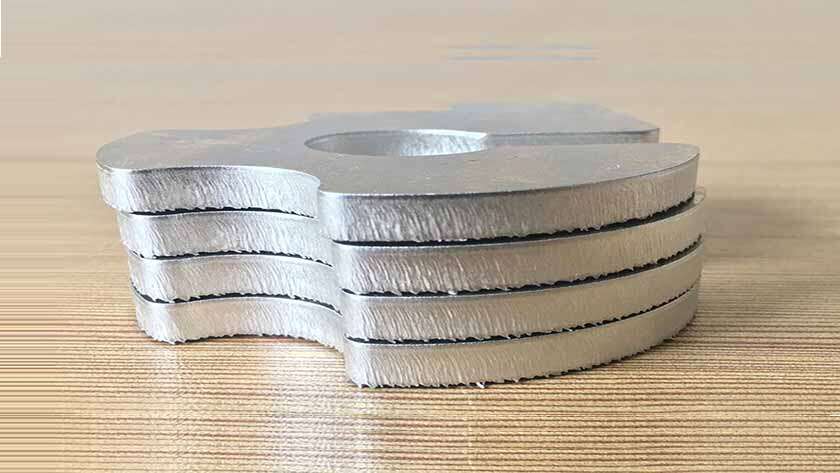

Burrs are remnants of material left behind after the cutting process, typically found at the bottom edges of the part during drilling or milling.
Cause:
During the cutting process, the final layer of material often deforms and moves away from the cutting tool, resulting in the formation of sharp burrs that adhere to the edges.
Solution:
To tackle the issue of burrs, you can employ the following solutions:
- Manual Removal: The simplest way to remove burrs is through manual deburring, where the excess material is carefully removed using appropriate tools.
- Thermal Deburring: Thermal deburring involves subjecting the workpiece to high temperatures and rapid cooling, causing the burrs to separate and fall off.
- Vibratory Deburring: Vibratory deburring utilizes vibrations to remove burrs from the workpiece. The workpiece is placed in a vibratory machine along with abrasive media, which effectively removes the burrs through friction.
Conclusion
CNC milling is a complex craft that demands expertise and experience. Even with years of practice, mistakes can still occur, potentially ruining a carefully milled part. For guaranteed precision and quality, it is advisable to rely on professional CNC milling services. By entrusting your projects to qualified machinists who possess in-depth knowledge of the craft, you can ensure flawless results without defects or imperfections.
Your Needed CNC Milling Solutions
At Want.Net, we have created an in-house environment of extreme accuracy. Our ISO 9001 certified CNC milling services are designed to support your important projects. Feel free to upload your CAD file for free quotations. For more information, please don’t hesitate to contact our team at [email protected].
Recommended Reads:
- Simplifying Complex Workpieces with CNC Machining Technology
- The Application of Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) in Modern Machine Shops
- How To Adapt Fixtures and Jigs for Intelligent Manufacturing
- How to Reduce the Cost of CNC Prototyping
- The Era of 5G: Transforming the World through Precision Machining
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Revolutionizing Renewable Energy with CNC Machined Components
Introduction: Renewable Energy and CNC Machined Components Renewable energy harnesses power from natural sources such as the sun, wind, and water, making it a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional…
- Is Copper the Right Choice for Electrical Component CNC Machining? A Detailed Analysis
CNC Machining of Electrical Components Utilizing Copper In the field of electrical engineering, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining plays an integral role, particularly in the development and manufacturing of electrical…
- CNC Machining Brass vs. Bronze: Cost, Properties, and Applications Showdown?
Introduction to CNC Machining Brass vs. Bronze: Cost, Properties, and Applications Showdown? In this article, we delve into the debate between brass and bronze machining for an important manufacturing process…