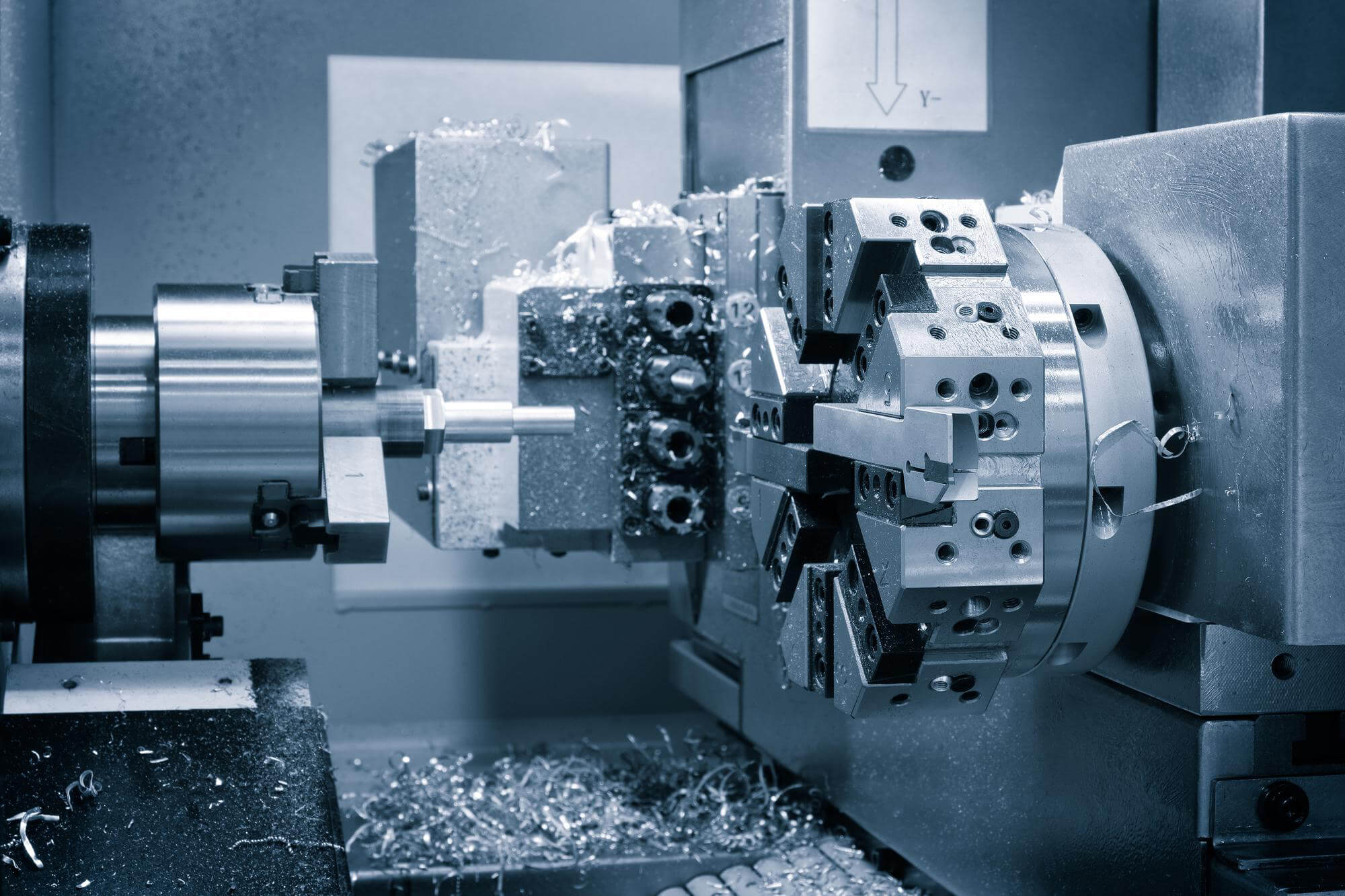
Walk into any machine shop, and you’ll likely see a variety of lathes humming away. These versatile machines are the backbone of many manufacturing processes, especially when it comes to CNC machining parts. CNC lathes, from standard two-axis machines to advanced multi-axis turning centers, offer incredible versatility and efficiency in machining parts. Their evolution from traditional lathes has transformed manufacturing, enabling the production of complex and precise parts with greater ease. By understanding the different types and their capabilities, manufacturers can choose the right CNC lathe for their needs and significantly enhance their production processes.
Traditional Lathes vs. CNC Lathes
Traditionally, machine shops have relied on standard lathes and turret lathes. These machines are designed for machining cylindrical and conical parts like shafts, rings, wheels, holes, and threads. The most common operation is removing material from a round workpiece using a cutting tool. While traditional lathes typically hold one or two cutting tools at a time, turret lathes come with a special tool holder that can accommodate several tools, although they have less machining power compared to standard lathes.
In the modern industrial world, CNC-controlled lathes, often referred to as CNC turning centers, have become more prevalent. These machines can perform a wide range of operations, from turning and boring to drilling, threading, knurling, and even polishing. They can handle different modes such as chuck work, collet work, and bar feeding, offering great versatility. CNC lathes are designed to hold multiple tools on a turret and often feature additional capabilities like milling attachments, indexing chucks, auxiliary axes, tailstocks, and steady rests.
Types of CNC Lathes
CNC lathes are classified based on their design and the number of axes they use. The two basic types are vertical CNC lathes and horizontal CNC lathes, with the latter being more common in manufacturing shops. Vertical CNC lathes, often mistakenly referred to as vertical boring mills, are less common but essential for machining large-diameter parts.
Classification by Axes:
- Two-Axis Lathes: The simplest and most common type, used for basic turning and boring operations.
- Three-Axis Lathes: Adds an additional axis for more complex machining.
- Four-Axis and Six-Axis Lathes: These provide greater flexibility for complex parts, allowing simultaneous operations and reducing setup times.
Horizontal CNC lathes can be further categorized by their design:
- Front Turret Lathes: The standard type, with the turret mounted in front of the workpiece.
- Rear Turret Lathes: Often featuring a slant bed design that keeps chips away from the operator and directs them towards a conveyor for easy disposal.
Benefits of Multi-Axis CNC Lathes
Multi-axis CNC lathes are becoming more popular due to their ability to perform multiple operations in a single setup. This reduces the need for multiple machines and setups, improving efficiency and precision. Here’s a table comparing the different types of CNC lathes:
| Type | Axes | Common Uses | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Two-Axis | 2 | Basic turning and boring | Simple design, cost-effective |
| Three-Axis | 3 | More complex parts, slight milling operations | Additional axis for enhanced flexibility |
| Four-Axis | 4 | Complex geometries, simultaneous operations | Increased flexibility, faster cycle times |
| Six-Axis | 6 | Highly complex parts, intricate machining | Maximum flexibility, reduces setups |
Practical Tips for Using CNC Lathes
- Tool Management: Efficiently manage and organize cutting tools to minimize downtime and ensure high-quality machining.
- Regular Maintenance: Perform routine checks and maintenance on your lathes to keep them in optimal working condition.
- Programming: Pay close attention to programming, especially when dealing with multi-axis operations. Use simulations to catch potential errors.
- Safety First: Always follow safety protocols, wear appropriate protective gear, and ensure the workspace is clean and free of hazards.
Real-World Example
Consider a company that manufactures custom automotive parts. Initially, they used traditional lathes, but as demand for more complex and precise parts grew, they upgraded to CNC turning centers. With the new CNC lathes, they were able to:
- Increase Production Efficiency: Multi-axis capabilities allowed for complete part machining in a single setup.
- Improve Precision: Advanced programming and stable machine design resulted in higher precision parts.
- Expand Capabilities: They could now produce a wider variety of parts, including those with complex geometries and fine details.
Related Posts
- Exploring the World of CNC Machining Parts: From Mills to Lathes
In today's manufacturing world, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are indispensable. These high-tech machines are capable of producing incredibly precise and complex parts, making them essential for industries ranging from…
- Impeller five-axis CNC precision machining technology
The impeller is the most important part on the rotor, and is generally composed of a wheel disc, a wheel cover and a blade. An integral impeller is an impeller…
- Choosing Between 3- and 5-Axis CNC Machining for Complex Aluminum Parts
Introduction to CNC Machining CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a manufacturing process that uses pre-programmed computer software to control the movements of factory tools and machinery. This technology plays…
- 3 Axis Vs 5 Axis CNC Machining: Custom Precision Parts Cost
In modern custom CNC machining services, the need for high precision customized machining parts is rising. No doubt, COVID-19 has also put an impact on the cost of parts ranging from…
- What are the requirements for CNC machining of bearing parts?
Bearings are common and important parts in the automotive industry, which can support transmission components and transmit torque. Generally, CNC machining centers are used to process bearing parts. So what…
- Evolution of Mills and Machining Centers: The Future of CNC Machining Parts
Stepping into the world of CNC machining, you quickly realize how pivotal mills and machining centers are in crafting precise parts. Over time, these machines have evolved significantly, transforming from…