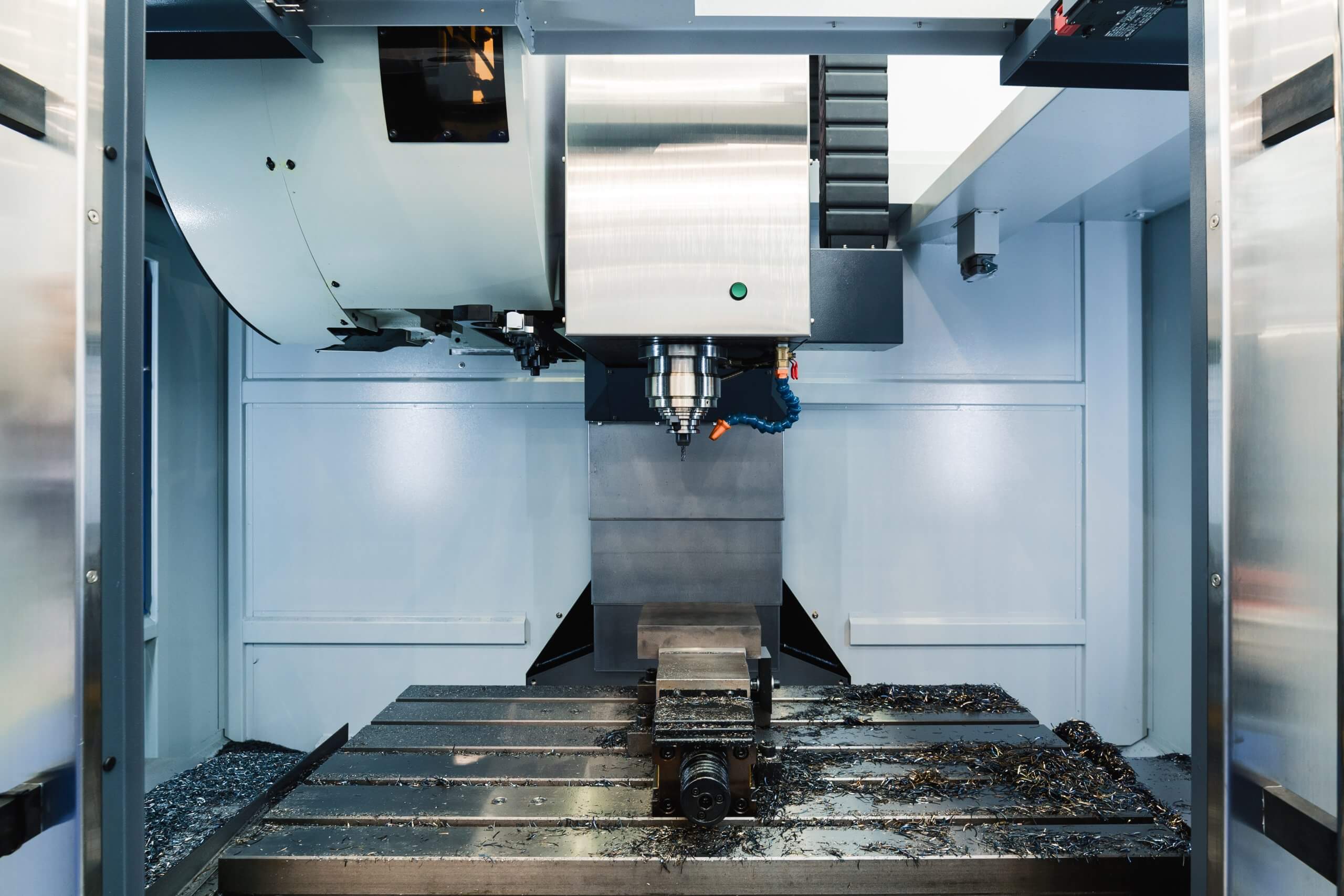
When you step into a machine shop, the hum of CNC machines is a familiar sound. Among these, the vertical CNC machining center is a workhorse, particularly when it comes to machining flat parts. Let’s take a closer look at what makes these machines tick, their unique features, and how to get the best out of them.
The Basics of Vertical CNC Machining Centers
Vertical CNC machining centers are primarily used for machining flat parts, like plates, where most operations are performed on a single side. The typical setup includes a table and a spindle that moves along the X, Y, and Z axes.
But there’s more! Many vertical CNC machines can be equipped with a fourth axis, usually a rotary head mounted on the main table. This fourth axis can be installed vertically or horizontally, depending on what you need. It adds flexibility by allowing either indexing or full rotational movement, which is super handy for long parts that need support at both ends.
Key Points for CNC Programming
When you’re programming these machines, there are a couple of things to keep in mind:
- Perspective Matters: Always consider the spindle’s viewpoint, not the operator’s. This means visualizing the tool movements from above, perpendicular to the table.
- Ignore Machine Markings: While there are markings indicating the positive and negative directions of the machine’s axes, these are for the operator. As a programmer, you should ignore these and focus on the programming directions, which are often the opposite.
Comparing Vertical and Horizontal Machining Centers
Here’s a quick comparison between vertical and horizontal machining centers to help you see how they stack up:
| Description | Vertical Machining Center | Horizontal Machining Center |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Axes | 3 (X, Y, Z) | 4 (X, Y, Z, B) |
| Table Dimensions | 780mm x 400mm (31in x 16in) | 500mm x 500mm (20in x 20in) |
| Tool Capacity | 36 | 40 |
| Max X-axis Travel | 575mm (22.5in) | 725mm (28.5in) |
| Max Y-axis Travel | 380mm (15in) | 560mm (22in) |
| Max Z-axis Travel | 470mm (18.5in) | 560mm (22in) |
| Spindle Speed | 60-8000 rpm | 40-4000 rpm |
| Spindle Power | AC 7.5/5.5 kW (10/7 hp) | AC 11/8 kW (15/11 hp) |
| Distance from Spindle to Table | 150-625mm (6-24.6in) | 150-710mm (6-28in) |
| Distance from Spindle to Column | 430mm (17in) | 30-560mm (1.2-22in) |
| Spindle Taper | No. 40 | No. 50 |
| Tool Holder Size | BT40 | CAT50 |
| Number of Pallets | N/A | 2 |
| Pallet Type | N/A | Rotary |
| Pallet Change Time | N/A | – |
| Pallet Indexing Angle | N/A | 0.001° |
| Rapid Feed Rate | 2-10000mm/min (0.1-393in/min) | 40000mm/min (XY), 35000mm/min (Z) (1575/1378in/min) |
| Tool Change Time | 2.5s | – |
Practical Tips and Tricks
- Keep it Clean: Always maintain a clean workspace. Metal shavings and oil spills can be hazardous and disrupt the machining process.
- Proper Safety Gear: Wear safety glasses, ear protection, and appropriate footwear. Avoid loose clothing and tie back long hair.
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure all guards and emergency stops are in place and functioning. Regularly check and maintain machines to prevent malfunctions.
- Effective Programming: Verify tool paths, use correct speeds and feeds, and run simulations to catch potential issues before they occur on the machine.
Vertical CNC machining centers are incredibly versatile and efficient, especially for flat parts. Whether you’re setting up a simple job or a complex one requiring a fourth axis, these machines can handle it. Remember to keep safety and cleanliness a priority, and make sure your programming is precise. With these tips in mind, you’ll be well on your way to mastering the use of vertical CNC machining centers.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Precision CNC Machining of Steel: High-Volume Production
Precision CNC Machining and High-Volume Production As an integral part of modern manufacturing processes, Precision Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining brings about unmatched accuracy and consistency in the production of…
- Material Versatility in CNC Machining: From Titanium to Thermoplastics
Introduction to CNC Machining CNC machining stands as a cornerstone in the manufacturing sector, enabling the precise creation of parts and components. This process utilizes computer numerical control (CNC) to…
- Precision CNC Machining for High-Performance Industrial Machinery
Precision CNC Machining for High-Performance Industrial Machinery The process of Precision CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is at the core of manufacturing high-performance industrial machinery. This technique leverages a computer's…
- Nickel vs. Cobalt Alloys in High-Temperature CNC Machining: A Detailed Analysis?
Nickel and Cobalt Alloys in High-Temperature CNC Machining Both Nickel and Cobalt alloys play an essential role in high-temperature CNC machining. These metal alloys are popular choices due to their…
- CNC Machining for Medical Applications: Compliance and Material Selection?
Introduction to CNC Machining in Medical Applications CNC or Computer Numerical Control machining is a manufacturing process wherein pre-programmed computer software dictates the movement of factory tools and machinery. This…
- Unraveling Bead Blasting Process in CNC Machining(cnc machining china Sid)
Bead blasting is a significant process within the realm of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining, providing numerous industries with quality finishes for various types of products. From aircraft parts to…