In the world of metals and alloys, bronze and brass are two materials that are often mentioned in the same breath. Despite their similarities, they are distinctly different in their compositions, properties, and applications. This article aims to demystify these differences, providing a comprehensive comparison between bronze and brass.
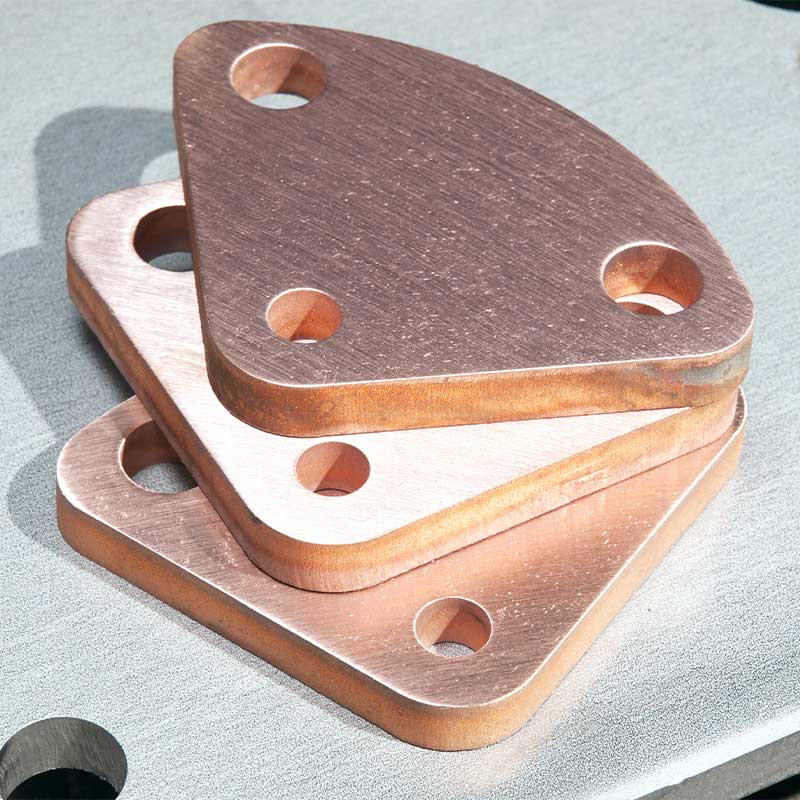
What is Bronze? Bronze, an alloy primarily composed of copper and tin, has been used since antiquity for various applications. Its composition can vary, but typically, it contains about 88% copper and 12% tin. Other elements like aluminum, nickel, and zinc can also be added to achieve different properties.
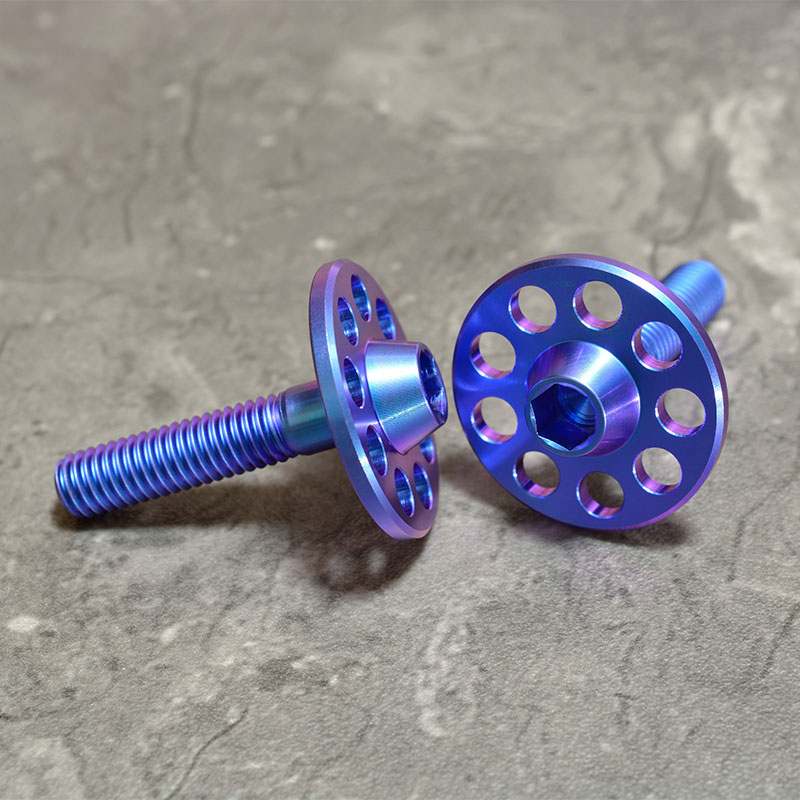
What is Brass? Brass, on the other hand, is primarily an alloy of copper and zinc. The proportion of zinc can vary between 5% and 45%, which significantly influences its properties. Brass may contain other elements like lead to improve machinability or tin to enhance corrosion resistance.
Key Differences Between Bronze and Brass
- Composition and Color
- Bronze: Copper and tin; offers a reddish-brown color.
- Brass: Copper and zinc; typically has a more yellowish hue.
- Properties
- Bronze: Generally harder and more brittle. It’s known for its durability and resistance to corrosion, especially against seawater. Bronze also has a lower melting point than brass.
- Brass: Softer and more malleable than bronze. It has good acoustic properties, making it popular in musical instruments. Brass’s malleability makes it easier to machine.
- Applications
- Bronze: Widely used in the creation of sculptures, medals, bearings, and gears. It’s also common in marine applications due to its corrosion resistance.
- Brass: Often found in musical instruments like trumpets and saxophones, as well as in decorative items, zippers, and plumbing materials.
- Machinability
- Bronze: Requires more force to machine due to its hardness and brittleness.
- Brass: Easier to machine and can be die-cast or worked in other forms easily.
- Acoustic Properties
- Bronze: Produces a clear, ringing sound, making it suitable for bells and cymbals.
- Brass: Known for its bright acoustic properties, hence its use in brass bands and orchestras.
- Cost
- Bronze: Generally more expensive due to the cost of tin.
- Brass: Less expensive, making it a more economical choice for large-scale applications.
- Corrosion Resistance
- Bronze: Highly resistant to corrosion, especially from saltwater, which makes it ideal for marine applications.
- Brass: Also resistant to corrosion, but its susceptibility increases in the presence of certain environments, like high salinity or low pH levels.
- Strength and Hardness
- Bronze: Typically stronger and harder, which contributes to its durability.
- Brass: Softer, which makes it more suitable for applications where it needs to be shaped or molded.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can bronze and brass be used interchangeably?
- Not always. The choice depends on the application’s specific requirements regarding strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic preferences.
- How can I tell the difference between bronze and brass?
- The easiest way is by color: bronze has a reddish-brown tint, while brass is more yellowish. A chemical test can also be conducted for a more accurate distinction.
- Which is heavier, bronze or brass?
- Generally, bronze is denser and heavier than brass, but the exact weight depends on the specific alloy composition.
Conclusion Bronze and brass, while similar in some respects, exhibit distinct differences in their composition, properties, and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate material for your specific needs. Whether you’re creating a musical instrument, a marine component, or a decorative item, choosing the right alloy can significantly impact the functionality and longevity of your product.
Embarking on a project and unsure whether to use bronze or brass? Consulting with a materials specialist can provide tailored advice, ensuring your project’s success. Remember, the right material choice is a crucial step in the journey from concept to creation.