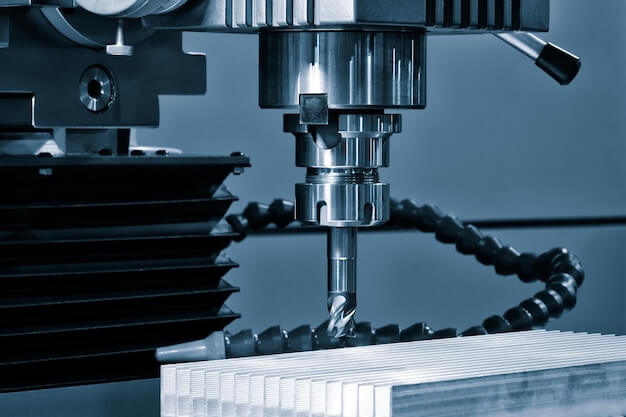
CNC Machining: An Essential Process Across Industries
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is a digital manufacturing technology that makes use of pre-programmed computer software to dictate the movement of various factory tools and machinery. The process allows for precise control of complex, three-dimensional cutting tasks across different materials such as plastics and metals. CNC machining plays a critical role in various industries including aerospace, automotive, medical, consumer goods, and construction – where its application ranges from production of prototypes to end-use parts leading to highly precise outputs and improved operational efficiency. For instance, in the automotive industry, it aids in producing high-precision gears and transmission components, thereby enhancing vehicle performance and safety.
Overview of Plastic CNC Machining
Plastic is a versatile material used extensively in Computer Numeric Control (CNC) machining due to its lightweight nature, ease of manipulation and cost-effectiveness. Using CNC technology, plastic can be shaped into precise components which find application in a multitude of industries such as automotive, medical, aerospace and more. Plastic CNC machined parts often include gears, enclosures, knobs among others.
The benefit of utilizing plastic lies not just in cost-efficiency but also in the ability to machine complex geometries with extreme precision that may otherwise prove difficult when working with metals. Another advantage of plastics involves their inherent resistance to corrosion, resulting in longer lifespan of the final product. However, there are certain limitations associated with plastic CNC machining. For instance, plastics have lower strength compared to metals making them unsuitable for high-stress applications. Also, certain types of plastic may warp or deform under excessive heat during the machining process.
Detailed Analysis of Metals Used in CNC Machining
When analyzing metals used in CNC machining, it’s important to consider various factors such as:
- Machining environment
- Part weight
- Heat resistance
- Electrical conductivity
- Magnetic requirements
- Hardness
- Surface finish
Comparing Plastic vs. Metal in CNC Machining
In CNC machining, both plastic and metal materials have their unique strengths and limitations that can greatly influence the efficiency, durability, cost-effectiveness, and overall complexity of design. Taking a closer look at each material’s attributes is essential for informed decision-making in specific use-case scenarios.
Primarily, plastic is often favoured due to its cost-effectiveness. It is relatively cheaper and easier to machine than metal, which implies a faster production speed. However, despite being lightweight, plastic may not provide the same level of durability as metal. Its typical applications include complex designs that require flexibility and thermal resistance such as protective covers or insulating parts.
- Metal, on the other hand, offers higher durability and sturdiness. Although more expensive to produce, it provides a long-lasting solution for heavyweight mechanical elements. The cost implications are justified by the longevity and robustness provided by metals like stainless steel or aluminium, making them ideal for structural components and machinery parts.
It’s important to note that the choice between these two materials highly depends on the application’s requirements for strength, budget, heat resistance, and expected product lifespan. Both serve distinctive needs based on these factors, hence ensuring effectiveness within their respective domains.
Key Factors for Choosing between Plastic and Metal CNC Machining
In the realm of CNC machining, determining whether to use plastic or metal material depends on several significant criteria. Firstly, intended application is critical in this decision-making process. For instance, if a product requires high-strength, corrosion resistance and excellent heat transfer characteristics, then your best bet would be metal CNC machining. On contrary, if you seek lightweight materials with good electrical insulation properties and lower costs, opt for plastics.
Budget plays another pivotal role as well. Due to differing production processes and raw material prices, there’s an inherent cost disparity between these two types of machining. While metal often ensues higher manufacturing cost its enhanced durability could entail lesser expenditures over the long haul. Meanwhile, even though plastic is generally cheaper but it may not offer comparable lifespan thereby driving potential recurring replacement expenses.
Lastly, the expected product lifespan should be considered. Metals, being hard-wearing typically last longer than their plastic counterparts. Therefore, for applications requiring longevity and endurance, metal would be fitting. However, employing plastic can serve adequacy for short-term uses.
Conclusion
In the debate of Plastic vs. Metal CNC Machining, it’s increasingly apparent that each has its unique advantages and ideal applications. Whether you prioritize durability, cost-effectiveness, or aesthetic values will significantly influence the choice between metal and plastic materials for your CNC machining project.
The key takeaway from this comparison is that both types of material have their strengths and weaknesses–plastic provides a lightweight, affordable option with high corrosion resistance while metals are unmatched in terms of strength, thermal properties, and overall durability. They can be used interchangeably based upon specific project needs rather than one being universally superior to the other.
Rather than harboring preconceived notions about the superiority of either plastic or metal, manufacturers must thoroughly assess the requirements of their individual projects. Effects on performance, longevity, and feasibility should play deciding roles when choosing your material for CNC machining. Thus making informed decisions can ensure optimal results in line with particular project specifications.
Understanding the Differences between Plastic and Metal CNC Machining
Before delving into a detailed comparison between plastic and metal CNC machining, it is essential to decode commonly faced confusion among users arising from a generalised lack of understanding of these two types. While both procedures follow similar steps, their innate material properties often dictate when one should be preferred over the other.
For instance, plastic CNC machining affords an impressive ability for high precision production of complex parts at considerably lower weights compared to metals. This makes them a popular choice in industries like electronics or healthcare where weight-sensitive applications are prevalent. However, their reduced durability under heavy load conditions can occasionally limit application scope.
On the other hand, the inherent toughness and superior heat resistance offered by metals make them better suited for higher stress environments such as automotive or aerospace industry use-cases. The strength associated with metals does come with its own set of challenges though, mainly resulting in longer lead times due to slower cutting rates being needed to avoid potential damage. These inherent distinctions impose a critical need to carefully choose the ideal material based on the specific project requirements.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Custom CNC Machining for High-Tech Security Systems
Introduction to CNC Machining for High-Tech Security Systems Custom Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining plays an integral role in the production of high tech security systems. It is a manufacturing…
- Revolutionizing CNC Machining for the Future of Smart Wearables
Introduction: CNC Machining and Smart Wearables CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a manufacturing process that utilizes computerized controls to operate and manipulate machine tools, converting raw materials into finished…
- Tool Steel Grades for CNC Machining: D2 vs. A2 - A Comparative Study?
Introduction to CNC Machining and Tool Steel CNC machining, or computer numerical control machining, is a manufacturing method that employs pre-programmed software to direct the activity of factory tools and…